
Stage 1 : Degeneration
As the disc dehydrates with age, it begins to lose elasticity and becomes brittle.
Treatment Time : 2 Month
Sesssion Required : 10


During a traumatic injury, your spine may lurch forward forcefully causing your vertebrae to compress the front of one or more of your lumbar discs beyond normal limits. As a result, the back of your disc protrudes backward. Causing small tears and thinning of your annulus fibrosis. Over time your damaged annulus fibrosis may weaken and change shape. And your nucleus proposes may dry out and lose flexibility. As your intervertebral discs deteriorate your nucleus proposes may pusher annulus outward resulting in a disc bulge. Depending on its location the bulge may push on or impinge one of your spinal nerves or spinal cord or your cauda Equina which is a collection of spinal nerve roots at the end of your spinal cord. Central disc bulges protrude backward into your spinal canal. Lateral disc bulges extend into your neural foramen. Severe lumbar disc injuries can tear your annulus fibrosis. Pressure from your vertebrae may push your nucleus proposes out of your torn annulus causing a disk herniation. A herniated lumbar disc can impinge upon your cauda equina or spinal nerves and cause symptoms such as pain numbness or weakness in one or both of your legs.








As the disc dehydrates with age, it begins to lose elasticity and becomes brittle.
Treatment Time : 2 Month
Sesssion Required : 10

Over time tiny tears may form in the outer, fibrous ring (annulus fibrosus) of an intervertebral disc allowing the soft, gel-like central portion (nucleus pulposus) to bulge out or produce a "bubble" along the tough fibrous outer layer.
Treatment Time : 4 Month
Sesssion Required : 20

Next, a disc extrusion occurs when part of the nucleus breaks through the tough fibrous outer layer (annulus fibrosus ) but still remains within the disc. This type of lumbar herniation may also be referred to as a non-contained herniation or trans-ligamentous herniation.
Treatment Time : 6 Month
Sesssion Required : 30

Finally, a disc sequestration occurs when the leaking gel-like material (nucleus pulposus) breaks through the tough outer layer (annulus fibrosus) and is loose within the spinal canal. This may also be referred to as a free fragment.
Treatment Time : 9 Month
Sesssion Required : 45





A slipped disc occurs when the gel covering a disc in the spine herniates and shifts, due to degeneration of disc elasticity. A slipped disc is also known as a ‘herniated’ disc.

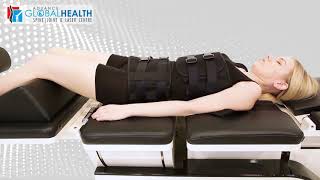
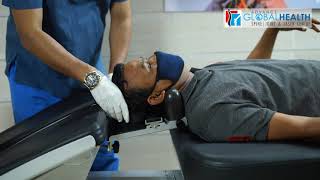
The laser beam is applied to the Lower Back of the Spine.

After some sittings, Disc comes to its Regular Position.

WE ARE RELIABLE & TRUSTED














Step 1 : Lie face down on the mat, with your elbows below your shoulders, and hands forward in line with your torso.
Step 2 : Next, press down onto the mat with both hands and forearms as you raise your head, shoulders and chest off the ground. Feel a gentle stretch on the stomach muscles as you lengthen your spine. Remember to keep both palms and both legs pressed firmly onto the floor. Hold your position for 8 to 10 seconds,.
Step 3 : Then release and go back down to starting position. Repeat this set for ten times.
Step 1 : Lie on your back bend one knee.
Step 2 : Pull the leg over keeping the knee very slightly bent until a gentle stretch is felt at the back of the leg. Perform 3 sets of 10 seconds once or twice a day.
Step 1 : Sit on the floor or a prop with the soles of your feet pressing into each other.
Step 2 : To deepen the intensity, move your feet closer in toward your hips. Root down into your legs and sitting bones. Elongate and straighten your spine, tucking your chin in toward your chest. Hold this position for up to 2 minutes.
Step 1 : Get onto the hands and knees with the knees hip-width apart.
Step 2 : Arch the back, pulling the bellybutton up toward the spine.
Step 3 : Slowly relax the muscles and allow the abdomen to sag toward the floor.
Step 4 : Return to the starting position. 5. Repeat 3–5 times twice a day.
Step 1 : Kneel on the floor with knees about as wide as your hips and sit on your heels.
Step 2 : Flex forward at the hips, bringing your heart and chest between or on top of your thighs. Keep your arms extended forward, remembering to keep your buttocks in contact with your heels. Hold for 20 to 30 seconds and repeat.
Step 1 : Sit with one leg extended and the other leg folded behind with your foot towards your glutes.
Step 2 : Fold over at the waist and reach for the shin or the foot.
Step 3 : Roll back up to the seated position. Repeat with the other leg.
Step 1 : Begin in a half-kneeling position with your right leg in front and left knee grounded.
Step 2 : Squeeze the glutes on the left side to help release the hip flexors on the left, shifting your weight slightly forward.
Step 3 : To add to this stretch, reach your left arm overhead and gently bend your torso toward the right. Hold for 45 seconds and repeat on the other side.
Step 1 : Lie on your back with your knees bent, and both feet flat on the floor. Place the right ankle on top of the left knee creating a figure-4.
Step 2 : Gently pull the left thigh toward your chest. You can grasp the back of the left thigh, or the front of the shin. Hold stretch for 20 to 30 seconds and repeat on the other side.








