
Stage 1 : Acute Sciatica
Acute sciatica is a recent onset, 4 to 8-week duration of sciatic nerve pain. The pain may be self-managed and may not typically require medical treatment.
Treatment Time : 4 Month
Sesssion Required : 20


The spine is divided into 4 sections cervical thoracic lumbar and sacrum and coccyx. A typical vertebra consists of a vertebral body and a vertebral arch has processes for articulate and muscular attachment. The sciatic nerve is one of the body's major nerves it begins from a group of spinal nerves at the base of the spine runs under the piriformis muscle and then extends down into the thigh and leg. The sciatic nerve supplies sensation to the skin of the leg and foot it also supplies the muscles in the back of the thigh under the calf. Sciatica nerve pain can be caused by a lumbar herniated disc in the sciatic nerve, it’s regulating pain in buttocks and foot. Piriformis muscle syndrom, a small muscle that lies deep in the buttocks, becomes tight or spasms. This can put pressure on and irritate the sciatic nerve. Spinal stenosis is the abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal. This narrowing reduces the available space for the spinal cord and nerves. Spondylolisthesis is a slippage of one vertebra so that it is out of line with the one above it, narrowing the opening through which the nerve exits. The extended spinal bone can pinch the sciatic nerve. Osteoarthritis Bone spurs (jagged edges of bone) can form in aging spines and compress lower back nerves.







Acute sciatica is a recent onset, 4 to 8-week duration of sciatic nerve pain. The pain may be self-managed and may not typically require medical treatment.
Treatment Time : 4 Month
Sesssion Required : 20

Chronic sciatica is persistent sciatic nerve pain that lasts for more than 8 weeks and usually does not subside with self-management. Depending on the cause, chronic sciatica may require nonsurgical or surgical treatment.
Treatment Time : 9 Month
Sesssion Required : 35





Sciatica most commonly occurs when a herniated disk, bone spur on the spine, or narrowing of the spine (spinal stenosis) compresses part of the nerve.

This causes inflammation, pain and often some numbness in the affected leg.

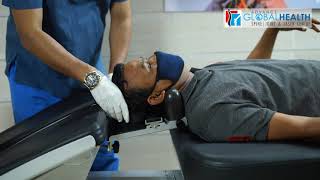
Laser Beam is applied to the spine and Sciatic nerve.

After some sittings, we get Healthy Disc & sciatic nerve

WE ARE RELIABLE & TRUSTED








Step 1 : Exercise can ease pain and inflammation. When you boost your heart rate, it also makes feel-good chemicals in your body. Any exercise is great. But you get a bonus from doing weight-bearing exercise -- when your joints have to support your weight, like when you walk instead of swim. It helps "feed" the cartilage in your joints and spine. Get your heart pumping most days of the week. Start with 5 to 10 minutes a day. Try to work up to 30 minutes or more.
Step 1 : Lie on your back bend one knee.
Step 2 : Pull the leg over keeping the knee very slightly bent until a gentle stretch is felt at the back of the leg. Perform 3 sets of 10 seconds once or twice a day.
Step 1 : Knee on the floor on all fours. Pick up your right leg and move it forward on the ground in front of your body. Your lower leg should be on the ground, horizontal to the body. Your right foot should be in front of your left knee while your right knee stays to the right.
Step 2 : Stretch the left leg out all the way behind you on the floor, with the top of the foot on the ground and toes pointing back.
Step 3 : Shift your body weight gradually from your arms to your legs so that your legs are supporting your weight. Sit up straight with your hands on either side of your legs. Support your weight with your arms as much as possible. Repeat on the other side.
Step 1 : Lie on your back with your legs extended and your feet flexed upward.
Step 2 : Bend your right leg and clasp your hands around the knee.
Step 3 : Gently pull your right leg across your body toward your left shoulder. Hold it there for 30 seconds.
Step 4 : Push your knee so your leg returns to its starting position. Repeat for a total of 3 reps, then switch legs.
Step 1 : While on your back, bring your right leg up to a right angle. Clasp both hands behind the thigh, locking your fingers.
Step 2 : Lift your left leg and place your right ankle on top of the left knee.Hold the position for a moment. This helps stretch the tiny piriformis muscle, which sometimes becomes inflamed and presses against the sciatic nerve, causing pain. Do the same exercise with the other leg.
Step 1 : Sit on the floor with your legs stretched out straight in front of you. Bend your right leg, putting your right ankle on top of the left knee.
Step 2 : Lean forward and allow your upper body to reach toward your thigh. Hold for 15 to 30 seconds. This stretches the glutes and lower back. Repeat on the other side.
Step 1 : Sit on the ground with your legs extended straight out with your feet flexed upward.
Step 2 : Bend your left knee and place your foot flat on the floor on the outside of your opposite knee.
Step 3 : Place your right elbow on the outside of your right knee
Step 4 : Gently turn your body toward the left. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat three times, then switch sides.
Step 1 : Place your right foot on an elevated surface at or below your hip level. This could be a chair, ottoman, or step on a staircase. Flex your foot so your toes and leg are straight. If your knee tends to hyperextend, keep a slight bend in it.
Step 2 : Bend your body forward slightly toward your foot. The further you go, the deeper the stretch. Don’t push so far that you feel pain.
Step 3 : Release the hip of your raised leg downward as opposed to lifting it up. If you need help easing your hip down, loop a yoga strap or long exercise band over your right thigh and under your left foot. Hold for at least 30 seconds, then repeat on the other side.








